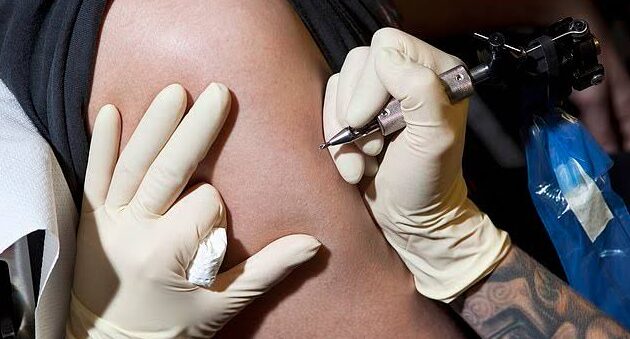
Oncologists and Haematologists have cautioned Nigerians against the new trend of getting tattoos, warning that the art, which is a type of body modification has been linked to an increased risk of blood cancers, particularly lymphoma – cancer of the blood.
The experts, who spoke exclusively with PUNCH Healthwise explained that certain chemicals in tattoo inks, including polyaromatic hydrocarbons known for their carcinogenic properties, may contribute to developing these blood cancers.
They warn that these carcinogenic chemicals can trigger an immune reaction in the body, leading to the development of blood cancers.
Recall that the 2024 Ojude Oba Day celebration gained significant social media attention, particularly with a cancer survivor identified as Farooq Oreagba, stole the show, capturing hearts with his charismatic presence
The highlight of the festival was when Oreagba, adorned in full aso-oke agbada regalia, emerged on his horse, complemented by a striking tattoo on his arm.
Photos and videos of Oreagba quickly circulated online, with many Nigerians expressing admiration for his tattoo and expressing interest in getting similar ones themselves.
However, experts in oncology and haematology quickly advised individuals with plans to get tattoos to be aware of the potential risks.
The physicians said that the process of tattooing involves injecting ink under the skin, where it can migrate into the lymphatic system and reach lymph nodes.
They explained that the presence of carcinogenic substances in these inks can lead to genetic damage and cellular changes that contribute to the development of lymphoma.
A Consultant clinical oncologist, Dr Charles Okwonna said the location and type of tattoo ink used are significant factors influencing the risk of developing blood cancers.
The cancer expert, who works at St. Luke’s Cancer Centre, United Kingdom, explained that the risk of developing blood cancers from tattoos is higher for people who have them placed near lymph nodes, such as the neck, armpits, and groin.
He said these were more likely to cause immune reactions due to higher chemical absorption in those areas.
He noted that the quality of ink and the tattooing process can increase the risk of developing blood cancers.
According to him, the quality of tattoo ink and the skill of the tattoo artist play crucial roles, adding that cheaper inks with more impurities may increase the risks.
Okwonna added, “Tattoo increases the risk of any of these blood cancers but it is more linked with lymphomas. This has been established recently.
“During the process of drawing tattoos, the ink that is used contains a carcinogenic or has been shown to contain a carcinogenic chemical, which we call the polyaromatic hydrocarbons, and these chemicals have been implicated also in cancers of other parts of the body, especially of the nasopharyngeal.
“Recently it has been shown through multiple studies, especially in Europe, that some of those inks contain these chemicals. What happens is, in the process of drawing the tattoo, these chemicals elicit some kind of complex reaction in the body, which we call an immunologic reaction.
“So, when the chemicals get injected into you either locally or sometimes, it gets absorbed through the little lymphatic channels around the skin area where you’re having it, it gets absorbed. Systemically, your body sees this as a foreign body trying to invade it and then elicits an immune reaction.
“The body elicits an immune reaction that tries to fight those chemicals. In the process of eliciting this immune reaction, over time, that immunity kind of gets exaggerated. When that happens, that’s when it starts to transform from being a normal immunologic reaction, to dysplasia (the presence of cells of an abnormal type within a tissue, which may signify a stage preceding the development of cancer), and then transform to a malignant immune reaction.”
He added, “What this means is that when you get an infection or when your body sees something coming to it like a foreign body, the body releases some cells, and these cells are immunologic. They include white blood cells, mast cells, and all that. So these cells’s basic work is to try to release some chemical substances that will fight those foreign things and prevent them from causing harm to the body.”
When asked about people more susceptible to getting cancer through tattoos, the oncologist explained that individual susceptibility to these immune reactions varies.
-Advertisement-
Grab our latest Magazine, "Ayodele Akintunde, SAN: Legal Titan Celebrates and Reflects on His Life Journey.". Get your order fast and stress free.
For more details about Newswire Law&Events Magazine, kindly reach out to us on 08039218044, 09070309355. Email: newswiremagazine@yahoo.co.uk. You will be glad you did